


Your gearbox
operation and maintenance expert1. Bearings Susceptible to Damage
Wind turbines are bulky and difficult to maintain, so they must be designed with a long service life, usually no less than 20 years. Most wind turbine failures occur in the gearbox, and the bearing in the gearbox is most prone to failure. Therefore, it is very important to choose the right bearing and accurately predict its service life that is often referred to as its fatigue life. A bearing will suffer surface spalling due to the contact between the rings and rolling body under alternating load. Such spalling is normal if it occurs outside the bearing’s service life, but unacceptable within the service life.
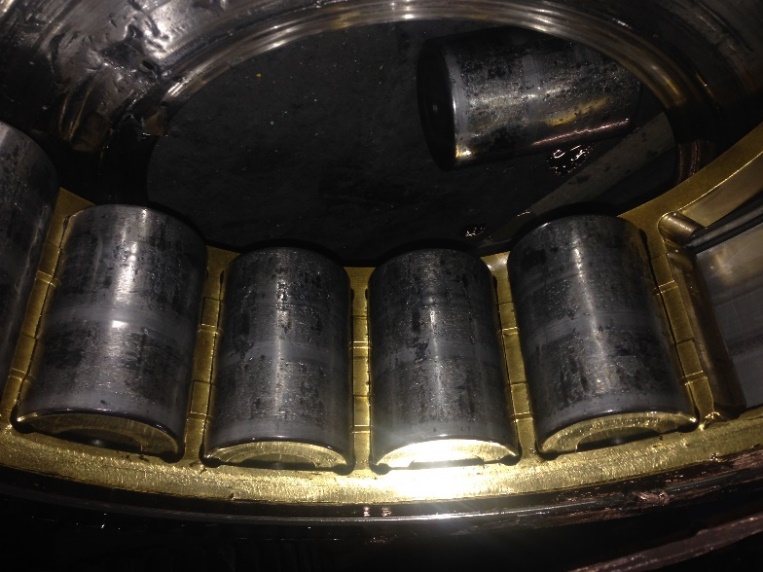

2. Incomplete Load Data
China is a vast country with many different weather systems, and in some places, wind turbines have to withstand harsh weather conditions and therefore extremely complex loads. However, when it comes to load data collection, China is still in a fledging period and it lacks well-developed methods for handling complex loads. For example, we estimate instantaneous loads, braking loads and ultimate loads merely based on past experience. In addition, the linear damage accumulation theory for determining variable loads is not mature, leading to unreasonable elementary calculations.
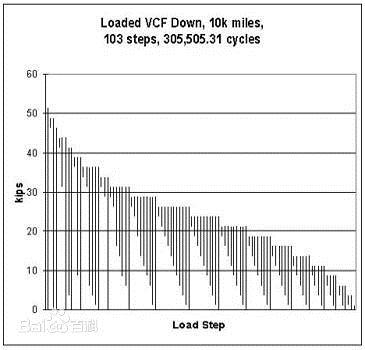
3. Immature Calculation Method
When designing wind turbines, we need to use a calculation model to determine the fatigue life of the gearbox bearing and then the fatigue strength of gears. The calculation model used in China is far less accurate than in developed countries. For example, the US uses gear rating standards AGMA 2101-C95 or ISO 6336:1996 as a design tool while China generally uses GB3480.
Conclusion: The gearbox in a wind turbine is under extremely complex loads, and it is the core and foundation of the whole wind turbine. To ensure wind turbines can work normally without interruption and failure, we must optimize the structure of the gearbox and give more thought to the design of bearings and other components.